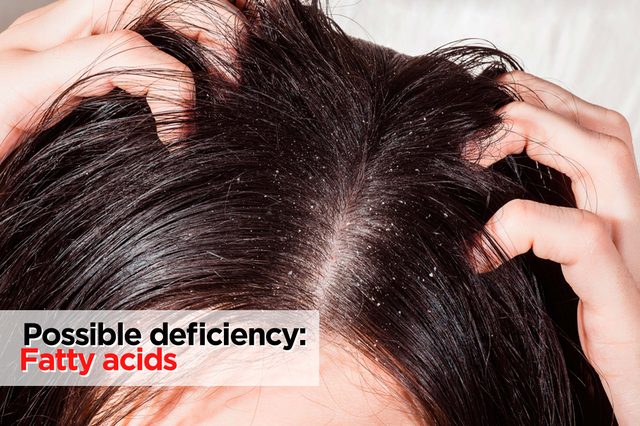
Flakey scalp
Possible deficiency: Fatty acids
If you notice that you’ve got flakes raining down after you scratch your head, you automatically think dandruff. But it may also be because you’re not getting enough healthful fatty acids in your diet. “Essential fatty acids, like omega-3s, are a lubricant for our body,” explains Staci Small, RD, of The Wellness Philosophy in Greenwood, Indiana. Without it, you’ll go dry. Make sure to eat two fish meals per week to get in omega-3s. Other fatty acids, like alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), are also important. Find these in walnuts and flaxseeds.

Thin, brittle hair
Possible deficiency: B vitamins
You hear all about how important the B vitamin biotin is for strong, healthy hair, and that’s true. However, running low on folate (also called folic acid) may also cause thin, brittle strands, says Small. Folate is often found in enriched grains like bread and cereal. Even one cup of white rice is an excellent source. But if you’ve been cutting out carbohydrates because you’re aiming to lose weight, you may be missing out without careful planning. Grains aren’t a must, though. A cup of raw spinach is a good source; a cup of cooked asparagus will give you 60 percent of your daily quota. Here are more signs you could be deficient in B vitamins.
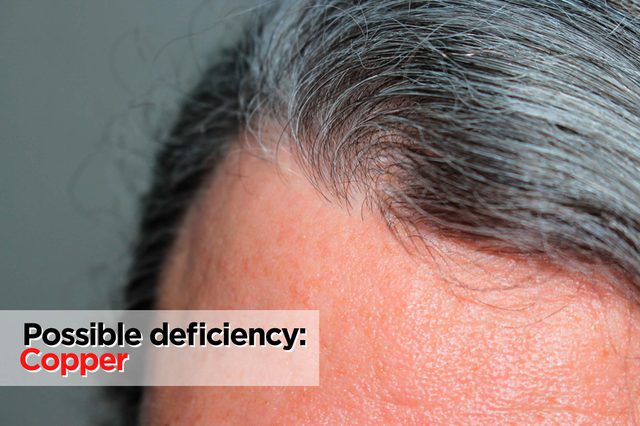
A graying part
Possible deficiency: Copper
If your part is looking unexpectedly silver lately, check your copper intake. “Copper plays a role in melanin production, which is what gives hair its color,” says Olivia Wagner, MS, RDN, LDN, of Aligned Modern Health, a group of functional wellness centers in Chicago. Consider getting your copper levels tested if your hair is going gray quickly or surprisingly early (like in your 20s without a family history). Canned clams, oysters, and mushrooms are all go-to sources. These are the vitamins you need to take at every age.
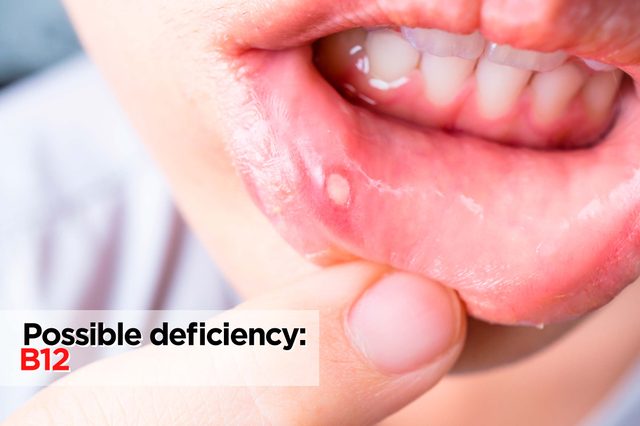
Cracks and sores in your mouth
Possible deficiency: B12
If your body needs more B12, you may notice that you’re getting ulcer-like lesions in your mouth or cracks on the sides. “I see people come in with this who have a B12 deficiency,” says Wagner. To correct that, she’ll look into a possible supplement, as well as advise adding more B12 sources into the diet. Get more poultry, (lean) red meat, and eggs. If you’re vegetarian, it’s a bit more of a challenge, but it’s doable with fortified foods, like non-dairy milk, cereal, and nutritional yeast. Here are more nutrients you could be missing if you’re vegetarian or vegan.
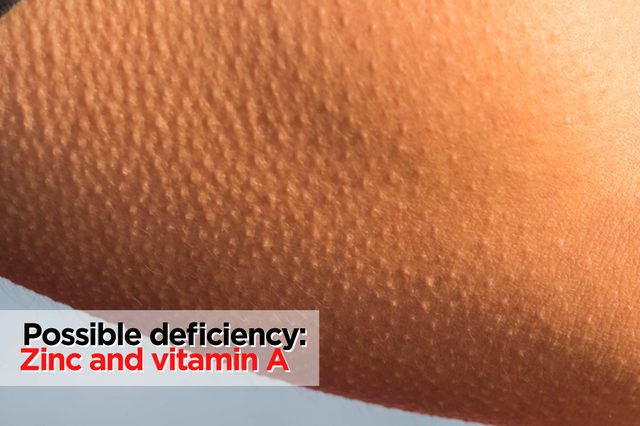
Bumps on the backs of arms
Possible deficiency: Zinc and vitamin A
If your arms aren’t super smooth but you don’t know why—and treating the bumps, a condition called keratosis pilaris, isn’t working well—something could be missing from your diet. “Many patients have these little red bumps that don’t itch. I always look at their zinc and vitamin A levels,” says Small. That’s because both nutrients are vital for maintaining skin health, and play key roles in wound repair. To get enough, you can find zinc in poultry, hummus, and pumpkin seeds. Get vitamin A from sweet potatoes and cantaloupe. Here’s the best time of day to take each of your supplements.
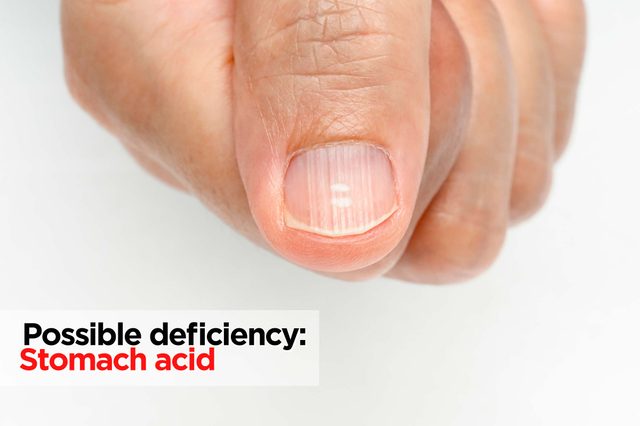
Fingernail ridges
Possible deficiency: Stomach acid
Having inadequate stomach acid doesn’t seem like a vitamin issue, but it can prevent you from breaking down nutrients in food and fully absorbing the vitamins and minerals you need. One possible cause: taking an over-the-counter heartburn medication, which will decrease your stomach acid, says Small. Some people find that taking some apple cider vinegar with water with a meal or taking a digestive enzyme (available as a supplement) can help. Bonus: “This can cut down on bloating after eating,” she says. Here are some more ways apple cider vinegar benefits your health.

Fatigue
Possible deficiency: Vitamin D
Being tired all the time, despite getting adequate sleep, is a red flag that your D is chronically low. If your doctor suggests you’d be a good candidate for a vitamin D supplement, studies show that they may be able to improve fatigue symptoms. (Though your doctor would advise you to take a much smaller dose daily.) “After people get more vitamin D, it’s amazing to hear them say they have so much more energy,” says Small. To fit more D into your diet, go for fortified dairy (yogurt, milk), non-dairy (almond or soy milk), certain fish (sardines), and even mushrooms grown under UV light.
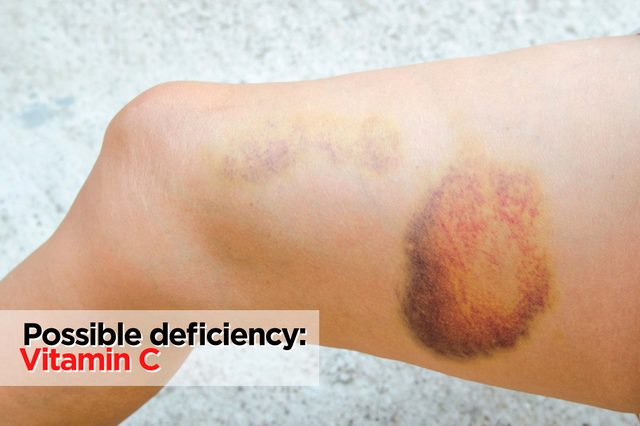
Bruising on your legs
Possible deficiency: Vitamin C
If you merely bump into something and wind up with an enormous bruise, consider if you’re getting enough C. Surprisingly, it’s on the list of nutrients Americans frequently fall short on, according to Health.gov. Vitamin C helps make collagen, which is involved in making blood vessels. Bruising often “may be a sign that you have weakened capillaries that allow you to bruise,” says Small. What’s more, stress saps your supply of vitamin C, meaning you may need more than you think. Strawberries, broccoli, and mango are all foods that have more C than an orange. Here are some foods high in vitamin C.

Calf cramps
Possible deficiency: Magnesium or calcium
As an electrolyte, magnesium plays an important role, along with and calcium, in muscle contraction. “Getting what you need can make a world of difference,” says Small. She recommends food sources such as pumpkin seeds, bananas, and avocados for magnesium. As for calcium, fortified non-dairy milk often contains more than its cow milk counterpart.

Constipation
Possible deficiency: Fiber and magnesium
Being backed up (having fewer than three bowel movements per week) has at least a dozen possible causes. One that’s common: a lack of fiber in the diet. In fact, adults consume just about half of the recommended 38 grams for men and 25 grams for women daily. Magnesium also plays a role in moving stool along, says Wagner. Along with eating more magnesium-rich foods, you may also consider a 120 mg supplement of magnesium citrate and increasing until regularity improves, she advises. And don’t forget the fiber. Good choices include lentils, broccoli, and apples. Next, find out the supplements you should be taking during cold and flu season.
